SARS-CoV-2
 Photo from the Internet
Photo from the Internet
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus was previously referred to by its provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19 or hCoV-19). First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January 2020, and a pandemic on 11 March 2020. SARS-CoV-2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is contagious in humans. As described by the US National Institutes of Health, it is the successor to SARS-CoV-1, the virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak.
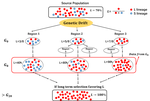
SARS-CoV-2 is a virus of the species severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV). It is believed to have zoonotic origins and has close genetic similarity to bat coronaviruses, suggesting it emerged from a bat-borne virus. Research is ongoing as to whether SARS‑CoV‑2 came directly from bats or indirectly through any intermediate hosts. The virus shows little genetic diversity, indicating that the spillover event introducing SARS‑CoV‑2 to humans is likely to have occurred in late 2019.
Epidemiological studies estimate that, in December 2019 — September 2020 period, each infection resulted in an average of 2.4 to 3.4 new ones when no members of the community are immune and no preventive measures are taken. The virus primarily spreads between people through close contact and via aerosols and respiratory droplets that are exhaled when talking, breathing, or otherwise exhaling, as well as those produced from coughs or sneezes. It mainly enters human cells by binding to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a membrane protein that regulates the renin-angiotensin system.
❤️ Related Research ❤️
- 👉 On the origin of SARS-CoV-2—The blind watchmaker argument
- 📚 A theoretical exploration of the origin and early evolution of a pandemic
- 💬 Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 in Italy, November 2019 and September 2019
- 💡 Others to be added